1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
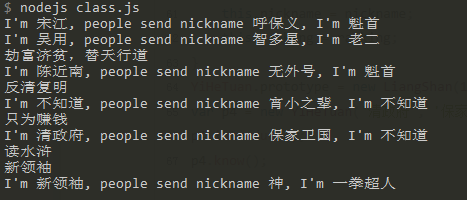
function LiangShan(name, nickname, ranking)
{
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
this.ranking = ranking;
this.introduce = function () {
console.log('I\'m ' + this.name + ', people send nickname ' + this.nickname + ', I\'m ' + this.ranking);
}
}
var p = new LiangShan('宋江', '呼保义', '魁首');
p.introduce();
LiangShan.work = function () {
console.log('劫富济贫,替天行道');
}
var p1 = new LiangShan('吴用', '智多星', '老二');
p1.introduce();
LiangShan.work();
LiangShan.prototype.know = function () {
console.log('读水浒');
}
LiangShan.prototype.time = '宋朝';
LiangShan.prototype.getName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
}
function HongHuaHui(name, nickname, ranking)
{
LiangShan.call(this, name, nickname, ranking);
this.task = function()
{
console.log('反清复明');
}
}
function HongMen(name, nickname, ranking)
{
HongHuaHui.apply(this, arguments);
this.task = function ()
{
console.log('只为赚钱');
}
}
var p2 = new HongHuaHui('陈近南', '无外号', '魁首');
p2.introduce();
p2.task();
var p3 = new HongMen('不知道', '宵小之辈', '不知道');
p3.introduce();
p3.task();
function YiHeTuan(name, nickname, ranking) {
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
this.ranking = ranking;
}
YiHeTuan.prototype = new LiangShan(1,2,3);
var p4 = new YiHeTuan('清政府', '保家卫国', '不知道');
p4.introduce();
p4.know();
function Group(name, nickname, ranking)
{
LiangShan.apply(this, arguments);
}
Group.prototype = new LiangShan();
var p5 = new Group('新领袖', '神', '一拳超人');
p5.getName();
p5.introduce();
|