通过将稀疏矩阵类型的二维数组通过技术手段生成的可以节省内存的数据结构,称为稀疏数组。稀疏数组归根结底还是一个数组,只不过对重复值较多的二维数组进行整理,达到降低存储空间的要求。当然,目标数组需要有一定的要求,下面通过实用的例子说明:
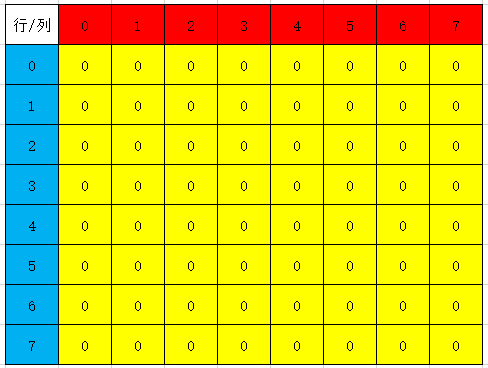
在五子棋游戏中,需要对每一个步骤的棋盘进行存储,定义棋盘为8×8的棋盘,0代表无子,1代表黑子,2代表白子。初始化棋盘后,如果使用原始数组保存棋盘数据,至少需要64个存储单元,如下图所示:

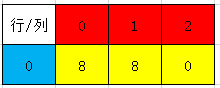
如果使用稀疏数组进行存储这个棋盘,最少只需要3个存储单元就可以完成,如下图所示:

下面说明转化步骤(注意[x,y]中的x,y分别表示行号,列号):
- 稀疏数组[0,0]位置存储的是二维数组中的行数
- 稀疏数组[0,1]位置存储的是二维数组中的列数
- 稀疏数组[0,2]位置存储的是二维数组中有效数据的个数(按五子棋的逻辑来说,就是有子的点的个数)
- 稀疏数组从第1行开始,每行存储的就是每一个数据的位置,其中第1列为行号;第2列为列号;第三列为数据的值
- 稀疏数组最小时只需要3个存储单元,最大的时候需要(n+1)*3个存储单元,n表示原始数组中的数据个数,所以稀疏数组通常用来存储数据重复值较多的数据。
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
| package SparseArray;
public class ChessBoard {
private int row;
private int col;
private int pieceCount = 0;
private int[][] chessboard;
public ChessBoard(int row, int col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.chessboard = new int[row][col];
}
public void addBlack(int row, int col) {
int piece = 1;
this.putPiece(row, col, piece);
}
public void addWhite(int row, int col) {
int piece = 2;
this.putPiece(row, col, piece);
}
protected void putPiece(int row, int col, int piece) {
if (this.pieceCount >= this.row * this.col) {
throw new RuntimeException("棋盘中棋子已满");
}
if (1 != piece && 2 != piece) {
throw new RuntimeException("棋子标记格式有误");
}
if (row > this.row) {
throw new RuntimeException("不符合规范的列号");
}
if (col > this.col) {
throw new RuntimeException("不符合规范的行号");
}
if (0 != this.chessboard[row][col]) {
throw new RuntimeException("此处位置已经被占用");
}
this.chessboard[row][col] = piece;
this.pieceCount++;
}
public void print() {
for (int[] rowItem : this.chessboard) {
for (int item : rowItem) {
System.out.printf("%d \t", item);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public int[][] toSparseArray() {
int[][] sparseArray = new int[this.pieceCount + 1][3];
sparseArray[0][0] = this.col;
sparseArray[0][1] = this.row;
sparseArray[0][2] = this.pieceCount;
int index = 1;
for (int row = 0; row < this.row; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < this.col; col++) {
if (0 != this.chessboard[row][col]) {
sparseArray[index][0] = row;
sparseArray[index][1] = col;
sparseArray[index][2] = this.chessboard[row][col];
index++;
}
}
}
return sparseArray;
}
public void printSparseArray() {
int[][] sparseArray = this.toSparseArray();
for (int[] items : sparseArray) {
for (int item : items) {
System.out.printf("%d \t", item);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| package SparseArray;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChessBoard chessBoard = new ChessBoard(8, 8);
System.out.println("初始化后的棋盘原始数组数据格式");
chessBoard.print();
System.out.println("初始化后的棋盘稀疏数组数据格式");
chessBoard.printSparseArray();
System.out.println("============================");
System.out.println("============================");
chessBoard.addBlack(4, 4);
chessBoard.addWhite(4, 5);
chessBoard.addBlack(5, 5);
chessBoard.addWhite(3, 3);
System.out.println("下棋中途的棋盘原始数组数据格式");
chessBoard.print();
System.out.println("下棋中途的棋盘稀疏数组数据格式");
chessBoard.printSparseArray();
}
}
|