数据结构从存储结构上分为顺序存储结构和链式存储结构,顺序存储结构的典型代表就是JAVA/C/C++等语言中的数组,而链式存储结构典型代表就是链表。链表属于链式存储结构,同时也属于线性结构(想了解结果分类的朋友可以查看上一篇博客)。
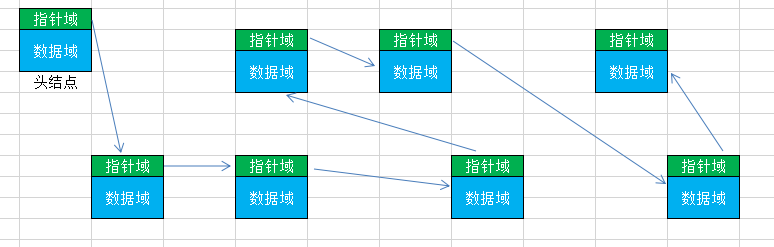
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。 相比于线性表顺序结构,操作复杂。由于不必须按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到O(1)的复杂度,比另一种线性顺序表(JAVA/C/C++等语言中的数组)快得多,但是查找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要O(n)的时间,而线性表和顺序表相应的时间复杂度分别是O(logn)和O(1)。
使用链表结构可以克服线性顺序表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。但是链表失去了线性顺序表随机读取的优点,同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大。链表最明显的好处就是,常规数组排列关联项目的方式可能不同于这些数据项目在记忆体或磁盘上顺序,数据的存取往往要在不同的排列顺序中转换。链表允许插入和移除表上任意位置上的节点,但是不允许随机存取。链表有很多种不同的类型:单向链表,双向链表以及循环链表。链表可以在多种编程语言中实现。像Lisp和Scheme这样的语言的内建数据类型中就包含了链表的存取和操作。程序语言或面向对象语言,如C,C++和Java依靠易变工具来生成链表。
单链表
顾名思义,单链表就是单向链表,意思是链表的方向唯一。在单链表中,只能通过一个结点中的指针域获取到下一个结点的存储地址。
单向链表(单链表)是链表的一种,其特点是链表的链接方向是单向的,对链表的访问要通过顺序读取从头部开始;链表是使用指针进行构造的列表;又称为结点列表,因为链表是由一个个结点组装起来的;其中每个结点都有指针成员变量指向列表中的下一个结点。

在图中可以看出,结点的存储地址不是连续的,结点之间的关系是由指针域进行存储维护的。另外,一般情况下,链表中都会存在一个头结点(header),这个结点的数据域存储的数据定义为无效数据,该结点只是为了能够让用户获取到链表中数据的入口结点。链表的写法多种多样,在下面的示例中,通过JAVA的内部类作为结点对象,方便管理。另外,单链表的方法可以根据实际的需求进行相应的扩展。
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
| package LinkedList;
public class SingleLinkedList {
private SingleLinkedList.Node header;
public SingleLinkedList()
{
SingleLinkedList.Node node = new SingleLinkedList.Node();
this.header = node;
}
public void tailInsert(int value)
{
SingleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header;
while (null != lastNode.getNext()) {
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
lastNode.setNext(new SingleLinkedList.Node(value));
}
public void headInsert(int value)
{
SingleLinkedList.Node firstNode = this.header.getNext();
this.header.setNext(new SingleLinkedList.Node(value, firstNode));
}
public int deleteValue(int value, int count)
{
int deleteCount = 0;
SingleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header;
while (null != lastNode.getNext() && deleteCount < count) {
if (value == lastNode.getNext().getValue()) {
lastNode.setNext(lastNode.getNext().getNext());
deleteCount++;
continue;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return deleteCount;
}
public int replaceValue(int search, int replace, int count)
{
int replaceCount = 0;
SingleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (null != lastNode && replaceCount < count) {
if (search == lastNode.getValue()) {
lastNode.setValue(replace);
replaceCount++;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return replaceCount;
}
public boolean isExists(int value)
{
SingleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (null != lastNode) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
return true;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return false;
}
public int getIndex(int value)
{
SingleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
int index = 0;
while (null != lastNode) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
return index;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
index++;
}
return -1;
}
public void print()
{
SingleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (null != lastNode) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", lastNode.getValue());
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
System.out.println();
}
public class Node {
private SingleLinkedList.Node next = null;
private int value = 0;
public Node(int value, Node next)
{
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int value)
{
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
public Node()
{
}
public Node getNext()
{
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public int getValue()
{
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value)
{
this.value = value;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| package LinkedList;
public class LinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
singleLinkedList.headInsert(10);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(9);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(8);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(7);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(6);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(5);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(4);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(3);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(2);
singleLinkedList.headInsert(1);
System.out.println("头部插入10个数字");
singleLinkedList.print();
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(10);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(9);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(8);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(7);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(6);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(5);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(4);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(3);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(2);
singleLinkedList.tailInsert(1);
System.out.println("尾部插入10个数字");
singleLinkedList.print();
singleLinkedList.replaceValue(1, 2, 1);
singleLinkedList.replaceValue(3, 4, 2);
System.out.println("将第一个1改为2,将两个3改为4");
singleLinkedList.print();
int index = singleLinkedList.getIndex(3);
System.out.println("第一个3的位置是" + index);
singleLinkedList.deleteValue(4, 4);
System.out.println("删除4个4");
singleLinkedList.print();
}
}
|

双链表
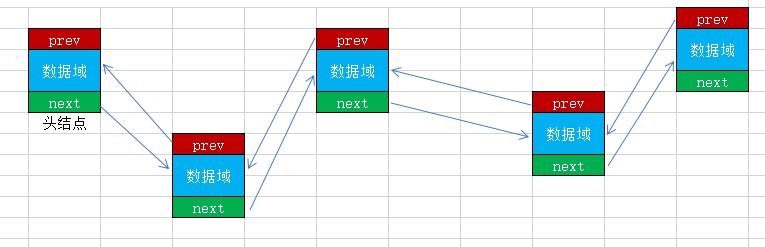
在上面的代码中,会发现在处理结点的过程中,只能通过指针域获取下一个结点,而不能反向查找。为了解决这个问题,可以在增加一个地址域,指向的是上一个结点,这样,在查找结点时会更加便捷,但是随之带来的问题是在维护结点关系时,会增加繁琐性。
双链表也叫双向链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表。

示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
| package LinkedList;
public class DoubleLinkedList {
private DoubleLinkedList.Node header;
public DoubleLinkedList()
{
DoubleLinkedList.Node node = new DoubleLinkedList.Node();
this.header = node;
}
public void tailInsert(int value)
{
DoubleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header;
while (null != lastNode.getNext()) {
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
lastNode.setNext(new DoubleLinkedList.Node(value, lastNode));
}
public void headInsert(int value)
{
DoubleLinkedList.Node newNode = new DoubleLinkedList.Node(value, this.header, this.header.getNext());
this.header.getNext().setPrev(newNode);
this.header.setNext(newNode);
}
public int deleteValue(int value, int count)
{
int deleteCount = 0;
DoubleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (null != lastNode && deleteCount < count) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
lastNode.getPrev().setNext(lastNode.getNext());
lastNode.getNext().setPrev(lastNode.getPrev());
deleteCount++;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return deleteCount;
}
public int replaceValue(int search, int replace, int count)
{
int replaceCount = 0;
DoubleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (null != lastNode && replaceCount < count) {
if (search == lastNode.getValue()) {
lastNode.setValue(replace);
replaceCount++;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return replaceCount;
}
public boolean isExists(int value)
{
DoubleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (null != lastNode) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
return true;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return false;
}
public int getIndex(int value)
{
DoubleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
int index = 0;
while (null != lastNode) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
return index;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
index++;
}
return -1;
}
public void print()
{
DoubleLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (null != lastNode) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", lastNode.getValue());
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
System.out.println();
}
protected class Node {
private DoubleLinkedList.Node next = null;
private DoubleLinkedList.Node prev = null;
private int value = 0;
public Node(int value, DoubleLinkedList.Node prev, DoubleLinkedList.Node next)
{
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
this.prev = prev;
}
public Node(int value, DoubleLinkedList.Node prev)
{
this.value = value;
this.prev = prev;
}
public Node(int value)
{
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
public Node()
{
}
public DoubleLinkedList.Node getNext()
{
return next;
}
public void setNext(DoubleLinkedList.Node next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public int getValue()
{
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value)
{
this.value = value;
}
public Node getPrev()
{
return prev;
}
public void setPrev(Node prev)
{
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package LinkedList;
public class LinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DoubleLinkedList doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList();
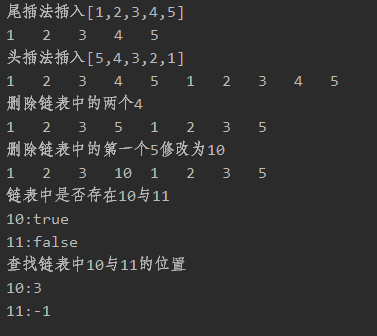
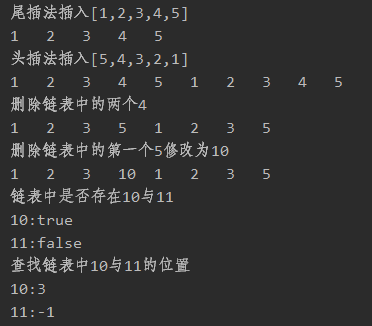
System.out.println("尾插法插入[1,2,3,4,5]");
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(1);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(2);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(3);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(4);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(5);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("头插法插入[5,4,3,2,1]");
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(5);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(4);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(3);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(2);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(1);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("删除链表中的两个4");
doubleLinkedList.deleteValue(4, 2);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("删除链表中的第一个5修改为10");
doubleLinkedList.replaceValue(5, 10, 1);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("链表中是否存在10与11");
System.out.println("10:"+doubleLinkedList.isExists(10));
System.out.println("11:"+doubleLinkedList.isExists(11));
System.out.println("查找链表中10与11的位置");
System.out.println("10:"+doubleLinkedList.getIndex(10));
System.out.println("11:"+doubleLinkedList.getIndex(11));
}
}
|

循环链表
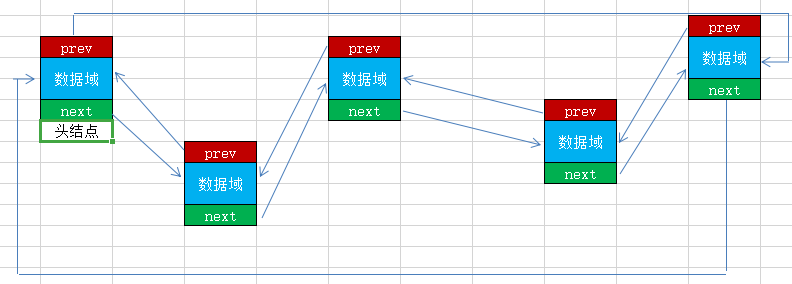
对链表进行再次改版,将链表中的尾部结点与链表中的头部节点设置为上下结点关系,则该链表就形成了环状的关系,称为环形链表,也称为循环链表。循环链表为解决部分算法中提供有效的帮助,例如著名的“约瑟夫环算法”。循环链表客户根据结点的指针域数量分为双向循环链表和单向循环链表。

代码示例
下面我们使用双向循环链表作为示例,需要注意的是,由于链表是一个环状的结构,所以一般不设置头部节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
| package LinkedList;
public class DoubleCircularLinkedList {
private DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node header;
public DoubleCircularLinkedList()
{
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node node = new DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node();
this.header = node;
this.header.setNext(this.header);
this.header.setPrev(this.header);
}
public void tailInsert(int value)
{
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header;
while (this.header != lastNode.getNext()) {
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node newNode = new DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node(value,lastNode, lastNode.getNext());
lastNode.getNext().setPrev(newNode);
lastNode.setNext(newNode);
}
public void headInsert(int value)
{
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node newNode = new DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node(value, this.header, this.header.getNext());
this.header.getNext().setPrev(newNode);
this.header.setNext(newNode);
}
public int deleteValue(int value, int count)
{
int deleteCount = 0;
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (this.header != lastNode && deleteCount < count) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
lastNode.getPrev().setNext(lastNode.getNext());
lastNode.getNext().setPrev(lastNode.getPrev());
deleteCount++;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return deleteCount;
}
public int replaceValue(int search, int replace, int count)
{
int replaceCount = 0;
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (this.header != lastNode && replaceCount < count) {
if (search == lastNode.getValue()) {
lastNode.setValue(replace);
replaceCount++;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return replaceCount;
}
public boolean isExists(int value)
{
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (this.header != lastNode) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
return true;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return false;
}
public int getIndex(int value)
{
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
int index = 0;
while (this.header != lastNode) {
if (value == lastNode.getValue()) {
return index;
}
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
index++;
}
return -1;
}
public void print()
{
DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.header.getNext();
while (this.header != lastNode) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", lastNode.getValue());
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
System.out.println();
}
protected class Node {
private DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node next = null;
private DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node prev = null;
private int value = 0;
public Node(int value, DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node prev, DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node next)
{
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
this.prev = prev;
}
public Node(int value, DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node prev)
{
this.value = value;
this.prev = prev;
}
public Node(int value)
{
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
public Node()
{
}
public DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node getNext()
{
return next;
}
public void setNext(DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public int getValue()
{
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value)
{
this.value = value;
}
public DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node getPrev()
{
return prev;
}
public void setPrev(DoubleCircularLinkedList.Node prev)
{
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package LinkedList;
public class LinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DoubleCircularLinkedList doubleLinkedList = new DoubleCircularLinkedList();
System.out.println("尾插法插入[1,2,3,4,5]");
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(1);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(2);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(3);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(4);
doubleLinkedList.tailInsert(5);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("头插法插入[5,4,3,2,1]");
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(5);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(4);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(3);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(2);
doubleLinkedList.headInsert(1);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("删除链表中的两个4");
doubleLinkedList.deleteValue(4, 2);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("删除链表中的第一个5修改为10");
doubleLinkedList.replaceValue(5, 10, 1);
doubleLinkedList.print();
System.out.println("链表中是否存在10与11");
System.out.println("10:"+doubleLinkedList.isExists(10));
System.out.println("11:"+doubleLinkedList.isExists(11));
System.out.println("查找链表中10与11的位置");
System.out.println("10:"+doubleLinkedList.getIndex(10));
System.out.println("11:"+doubleLinkedList.getIndex(11));
}
}
|

约瑟夫环问题
约瑟夫问题(有时也称为约瑟夫斯置换,是一个出现在计算机科学和数学中的问题。在计算机编程的算法中,类似问题又称为约瑟夫环。又称“丢手绢问题”.)
故事概况:在罗马人占领乔塔帕特后,39 个犹太人与Josephus及他的朋友躲到一个洞中,39个犹太人决定宁愿死也不要被敌人抓到,于是决定了一个自杀方式,41个人排成一个圆圈,由第1个人开始报数,每报数到第3人该人就必须自杀,然后再由下一个重新报数,直到所有人都自杀身亡为止。然而Josephus 和他的朋友并不想遵从。首先从一个人开始,越过k-2个人(因为第一个人已经被越过),并杀掉第k个人。接着,再越过k-1个人,并杀掉第k个人。这个过程沿着圆圈一直进行,直到最终只剩下一个人留下,这个人就可以继续活着。问题是,给定了和,一开始要站在什么地方才能避免被处决?Josephus要他的朋友先假装遵从,他将朋友与自己安排在第16个与第31个位置,于是逃过了这场死亡游戏。
为了解决这个问题,我们需要有一个循环链表,同时对链表的结构进行调整
- 为了便于查找数据,使用双向循环链表
- 删除链表中的头结点,增加一个指针结点,该指针结点作为获取链表中的数据的入口结点,该结点可以移动。当 链表为空时,指针结点pointer = null
- 外部可以通过方法移动指针指针结点。
- 结点域中的数据将自增(人的序号),不需要人为的传入数据域的数据
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
| package LinkedList;
public class JosephCircular {
private int count;
private int step;
private PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList personDoubleCircularLinkedList;
public JosephCircular(int count, int step)
{
this.count = count;
this.step = step;
this.personDoubleCircularLinkedList = new PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList();
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
personDoubleCircularLinkedList.add();
}
}
public void run()
{
if (this.personDoubleCircularLinkedList.count() < 2) {
System.out.println("最后一个被杀者" + this.personDoubleCircularLinkedList.getCurrentPointerIndex());
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i < this.step; i++) {
this.personDoubleCircularLinkedList.movePointer();
}
System.out.printf("第%d个人被杀死\n", this.personDoubleCircularLinkedList.getCurrentPointerIndex());
this.personDoubleCircularLinkedList.deleteMovePointer();
this.run();
}
class PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList {
private JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node pointer = null;
public void add()
{
if (null == this.pointer) {
JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node newNode = new JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node();
newNode.setIndex(1);
this.pointer = newNode;
this.pointer.setNext(this.pointer);
this.pointer.setPrev(this.pointer);
return;
}
JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.pointer;
while (this.pointer != lastNode.getNext()) {
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node newNode = new JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node();
int index = lastNode.getIndex() + 1;
newNode.setIndex(index);
newNode.setNext(lastNode.getNext());
newNode.setPrev(lastNode);
lastNode.getNext().setPrev(newNode);
lastNode.setNext(newNode);
}
public void movePointer()
{
if (null != this.pointer) {
this.pointer = this.pointer.getNext();
}
}
public void deleteMovePointer()
{
if (this.count() > 1) {
this.pointer.getPrev().setNext(this.pointer.getNext());
this.pointer.getNext().setPrev(this.pointer.getPrev());
this.pointer = this.pointer.getNext();
} else {
this.pointer = null;
}
}
public int count()
{
if (null == this.pointer) {
return 0;
}
JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node lastNode = this.pointer;
int count = 1;
while (this.pointer != lastNode.getNext()) {
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
count++;
}
return count;
}
public int getCurrentPointerIndex()
{
if (null == this.pointer) {
return -1;
}
return this.pointer.getIndex();
}
class Node {
private JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node next = null;
private JosephCircular.PersonDoubleCircularLinkedList.Node prev = null;
private int index;
public Node getNext()
{
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public int getIndex()
{
return index;
}
public void setIndex(int index)
{
this.index = index;
}
public Node getPrev()
{
return prev;
}
public void setPrev(Node prev)
{
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package LinkedList;
public class LinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
JosephCircular josephCircular = new JosephCircular(41, 3);
josephCircular.run();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| 第3个人被杀死
第6个人被杀死
第9个人被杀死
第12个人被杀死
第15个人被杀死
第18个人被杀死
第21个人被杀死
第24个人被杀死
第27个人被杀死
第30个人被杀死
第33个人被杀死
第36个人被杀死
第39个人被杀死
第1个人被杀死
第5个人被杀死
第10个人被杀死
第14个人被杀死
第19个人被杀死
第23个人被杀死
第28个人被杀死
第32个人被杀死
第37个人被杀死
第41个人被杀死
第7个人被杀死
第13个人被杀死
第20个人被杀死
第26个人被杀死
第34个人被杀死
第40个人被杀死
第8个人被杀死
第17个人被杀死
第29个人被杀死
第38个人被杀死
第11个人被杀死
第25个人被杀死
第2个人被杀死
第22个人被杀死
第4个人被杀死
第35个人被杀死
第16个人被杀死
最后一个被杀者31
|