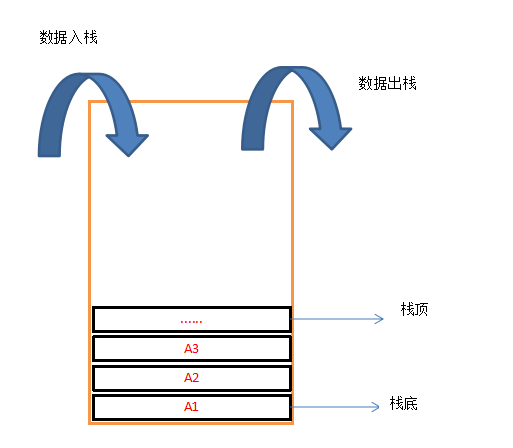
通过对队列的了解,我们知道队列是一种受限的线性表,数据出入的限制为“先进先出”。与队列对应的则是栈,栈也是一种受限的线性表,数据出入的限制为“先进后出”,与队列相同,我们可以称栈为“先进后出线性表”。
为什么栈要遵循“先进后出”的规则呢,因为栈的数据结构就像一个木桶一样,先入栈的数据在木桶底部,后入栈的数据在木桶顶部,在出栈的时候,后入栈的数据将优先被取出,所以造成了“先进后出”的现象。
- 栈顶:插入、删除数据的一端
- 栈底:栈顶的另一端,类似于木桶的底部
- 入栈(进栈、压栈):向栈中插入数据的动作
- 出栈(退栈):从栈中取出数据的动作

在JAVA中,已经存在内置好的栈对象,通常是不需要自己编写的。但是为了便于理解,我们自己编写一遍,这里使用数组进行模拟栈。
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| package Stack;
public class Stack {
private int[] data;
private int top = -1;
public Stack(int max)
{
this.data = new int[max];
}
public void push(int value)
{
if (this.isFull()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈已满");
}
this.data[++this.top] = value;
}
public int pop()
{
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈中不存在数据");
}
int value = this.data[this.top];
this.top--;
return value;
}
public int count()
{
return this.top + 1;
}
public boolean isFull()
{
return this.top == (this.data.length - 1);
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return this.top == -1;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package Stack;
public class StackMain {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stack stack = new Stack(5);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
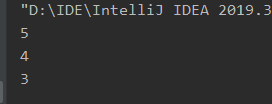
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
|