逆波兰算法是什么?逆波兰算法是通过将“中缀表达式”转化“后缀表达式”(也称为“逆波兰表达式”)的方式,实现一个公式的自动计算。
各类表达式
中缀表达式是一个通用的算术或逻辑公式表示方法。在日常生活中,我们所识所见的表达式通常都是中缀表达式。中缀表达式的操作符是以中缀形式处于操作数的中间(例如:3 + 4),而前缀表达式则是需要将操作符前置(例如:+ 3 4),而同理,后缀表达式则是将操作符后置(例如:3 4 +)。在人们的生活中,中缀表达式可以很方便的帮助人们快速计算,但是在计算机的语言中,中缀表达式的计算就不会这哪方便了。为了解决这一问题,波兰逻辑学家J・卢卡西维兹(J・ Lukasewicz)于1929年首先提出了一种表达式的表示方法,就是现在的“后缀表达式”,所以人们也称这一表达式为“逆波兰表达式”。
算法介绍
中缀转化为后缀的算法
- 初始化两个栈:运算符栈S(opera)和操作数栈S(num);
- 从左往右扫描中缀表达式
- 如果是数字那么将其直接入栈到S(num)中
- 如果是操作,需要进一步判断
- 如果是左括号’(‘直接入栈到S(opera)中
- 如果是运算符(’+’、’-‘、’*’、’/‘),先判断栈S(opera)的栈顶的操作数的优先级(如果是空栈那么直接入栈到S(opera))
- 如果是左括号那么直接入栈到S(opera)中
- 如果栈顶是运算符,且栈顶运算符的优先级大于等于该运算符.那么将栈顶的运算符出栈,并入栈到S(num)中,重复步骤3,
- 如果栈顶运算符优先级小于该运算符,那么直接将该运算符入栈到S(opera)中
- 如果是右括号’)’,那么说明在S(opera)栈中一定有一个左括号与之对应(在你没输错的情况下),那么将opera中的运算符依次出栈,并入栈到S(num)中,直到遇到左括号’(‘(注意左括号不用入栈到S(num))
- 如果中缀表达式扫描完了,那么将S(opera)中的操作数依次出栈,并入栈到S(num)中就可以了,如果没有没有扫描完重复1-3步
- 后缀表达式存在在S(num)中,如果想看一下后缀表达式的内容,可以从栈S(num)中依次取出数据,然后倒序展示。
后缀表达式的计算
- 初始化一个数字栈
- 从左至右扫描后缀表达式
- 遇到数字时,将数字压入堆栈,
- 遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数,用运算符对它们做相应的计算(次顶元素 op 栈顶元素),并将结果入栈;
- 重复上述过程直到表达式最右端,最后运算得出的值即为表达式的结果。
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
| package Rpn;
public class Rpn {
private Stack opera;
private Stack num;
public Rpn()
{
this.opera = new Stack(100);
this.num = new Stack(100);
}
public int calculate(String equation)
{
equation = this.toRpnEquation(equation);
String[] equationArray = equation.split(" ");
for (String chunk : equationArray) {
if (chunk.matches("\\d+")) {
this.num.push(chunk);
} else {
if (this.num.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("后缀表达式出错了:"+chunk);
break;
}
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(this.num.pop());
if (this.num.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("后缀表达式出错了:"+chunk);
break;
}
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(this.num.pop());
int result;
switch (chunk) {
case "+":
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case "-":
result = num2 - num1;
break;
case "*":
result = num2 * num1;
break;
case "/":
result = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
System.out.println("出错了,未知的计算操作式:"+chunk);
result = 0;
break;
}
this.num.push(String.valueOf(result));
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(this.num.pop());
}
protected String toRpnEquation(String equation)
{
String[] equationArray;
String chunk;
Stack num = new Stack(100);
Stack opera = new Stack(100);
while (equation.length() > 0) {
equationArray = this.fetchChunk(equation);
chunk = equationArray[0];
if (chunk.matches("\\d+")) {
num.push(chunk);
} else {
switch (chunk) {
case "(":
opera.push(chunk);
break;
case "+":
case "-":
case "*":
case "/":
while (true) {
if (opera.isEmpty()) {
opera.push(chunk);
break;
} else if ("(" == opera.peek()) {
opera.push(chunk);
break;
} else if (this.level(opera.peek()) >= this.level(chunk)) {
String op = opera.pop();
num.push(op);
} else {
opera.push(chunk);
break;
}
}
break;
case ")":
while (true) {
String top = opera.pop();
if (top.equals("(")) {
break;
}
num.push(top);
}
break;
}
}
equation = equationArray[1];
}
while (!opera.isEmpty()) {
num.push(opera.pop());
}
String rpnEquation = "";
while (!num.isEmpty()) {
rpnEquation = num.pop() + " " + rpnEquation;
}
return rpnEquation;
}
protected int level(String operator)
{
int level = 0;
switch (operator) {
case "+":
case "-":
level = 1;
break;
case "*":
case "/":
level = 2;
break;
default:
level = 0;
break;
}
return level;
}
protected String[] fetchChunk(String equation)
{
if (0 == equation.length()) {
return null;
}
String chunk = equation.substring(0, 1);
equation = equation.substring(1);
if (chunk.matches("\\d+")) {
while (equation.length() > 0) {
if (equation.substring(0, 1).matches("\\d+")) {
chunk = chunk + equation.substring(0, 1);
equation = equation.substring(1);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
String[] result = new String[2];
result[0] = chunk;
result[1] = equation;
return result;
}
protected class Stack {
private int max;
private String[] data;
private int top = -1;
public Stack(int max)
{
this.max = max;
this.data = new String[max];
}
public void push(String value)
{
if (this.isFull()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈已满");
}
this.data[++this.top] = value;
}
public String pop()
{
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
String value = this.data[this.top--];
return value;
}
public String peek()
{
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return this.data[this.top];
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return this.top == -1;
}
protected boolean isFull()
{
return (this.top + 2) == this.max;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package Rpn;
public class RpnMain {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Rpn rpn = new Rpn();
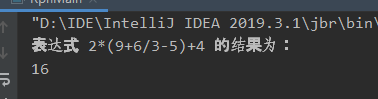
String equation = "2*(9+6/3-5)+4";
System.out.println("表达式 "+equation+" 的结果为:");
System.out.println(rpn.calculate(equation));
}
}
|