回溯算法实际上一个类似枚举的搜索尝试过程,主要是在搜索尝试过程中寻找问题的解,当发现已不满足求解条件时,就“回溯”返回,尝试别的路径。
在代码中,我们通常使用递归函数来实现回溯算法,所以可以通过递归函数来了解回溯算法的机制。下面通过经典案例《八皇后问题》来学习了解这一算法。
八皇后问题
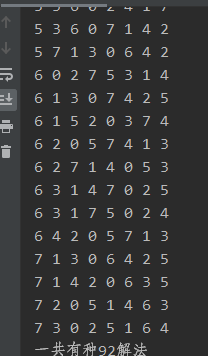
问题表述为:在8×8格的国际象棋上摆放8个皇后,使其不能互相攻击,即任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上,问有多少种摆法。高斯认为有76种方案。1854年在柏林的象棋杂志上不同的作者发表了40种不同的解,后来有人用图论的方法解出92种结果。
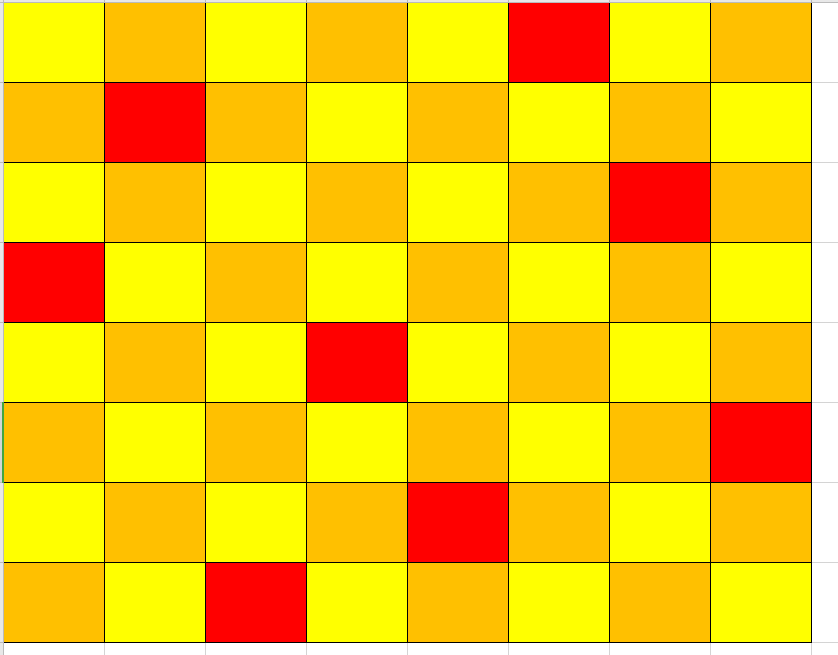
下图表示的是八皇后问题的其中一种解法,红色代表棋子位置,他们中每两个棋子既不在同一行,也不再同一列,还不在同一斜线。

回溯算法解决八皇后问题
通过回溯算法解决八皇后时,如果我们定义每个棋子的行为row;列为col;然后任意确认其中两个棋子分别为i,n。需要了解以下几点:
- 判断同一行的公式为 row(i)==row(n)
- 判断同一列的公式为 col(i)==col(n)
- 判断处于一个斜线上的公式为 abs(row(i)-row(n))==abs(col(i)-col(n))
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| package Queen8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Queen8 {
private int max = 8;
private int[] way = new int[max];
private ArrayList<int[]> result = new ArrayList();
public void run(int n)
{
if (n >= 8) {
this.result.add(this.way);
this.print();
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < this.max; i++) {
this.way[n] = i;
if (check(n)) {
this.run(n+1);
}
}
}
public void run()
{
this.run(0);
}
private boolean check(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (this.way[i] == this.way[n]) {
return false;
}
if (n - i == Math.abs(this.way[n] - this.way[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public ArrayList<int[]> getResult()
{
return result;
}
private void print()
{
for (int position : this.way) {
System.out.print(position + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import Queen8.Queen8;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Queen8 queen8 = new Queen8();
queen8.run();
System.out.printf("一共有种%d解法\t", queen8.getResult().size());
}
}
|